GRIHA Pre-certification rating is designed for projects intending to comply with the rating requirements in terms of the various criteria and their appraisals at design stage. It allows projects a room to reconsider and revamp their decisions based on critical parameters like design, equipment, material, and so on. Thereby strengthening the aspects of sustainability in the project to a greater level.
GRIHA Precertification Rating
Introduction
Intent
The GRIHA rating system promotes the built environment and sustainable habitat of green buildings for Indian climate zones.
Salients Features
Indigenous rating system
The system acknowledges the diverse climatic conditions of the country which become the underlying factor for the formulation of GRIHA rating. The rating system aims at providing inherent solutions for thermal comfort within each region.
Adoption of holistic approach towards sustainability
The rating system was developed with the intent to promote sustainability by not just underlining the environmental aspects but also focusing on the social and economic aspects as well.
Process driven and performance oriented
Every stage of construction, starting from design conception to execution, is vital to achieve sustainability. GRIHA takes into account all the stages, including design, procurement, and implementation to avoid disruption to the ecological system and construct high-performing sustainable structures.
Integrated team approach
With the aim to interact with the project team and guide them through the rating process, an orientation workshop is conducted by GRIHA Council where representatives from different divisions handling the project are present to understand their role in making the project GRIHA compliant.
Benefits/Advantages of adopting GRIHA Precertification Rating
Reduced Energy Consumption
Encourages passive design strategies, energy-efficient systems, and renewable energy integration to reduce operational energy use.
Water Conservation
Promotes rainwater harvesting, wastewater treatment, and water-efficient fixtures to reduce water consumption.
Waste Reduction
Incorporates solid waste management, construction waste minimization, and waste reuse and recycling to convert waste to resource.
Lower Carbon Footprint
Encourages low-embodied energy materials and operational efficiency to reduce GHG emissions.
Lower Operating Costs
Reduced energy and water use directly translating into long-term savings for occupants and owners.
Enhanced Asset Value
Sustainable buildings offer higher marketability and occupancy rates.
Eligibility for Incentives
Governments offer fast-track approvals, extra FAR, and tax rebates for GRIHA-rated projects.
Eligibility & Virtual Boundary
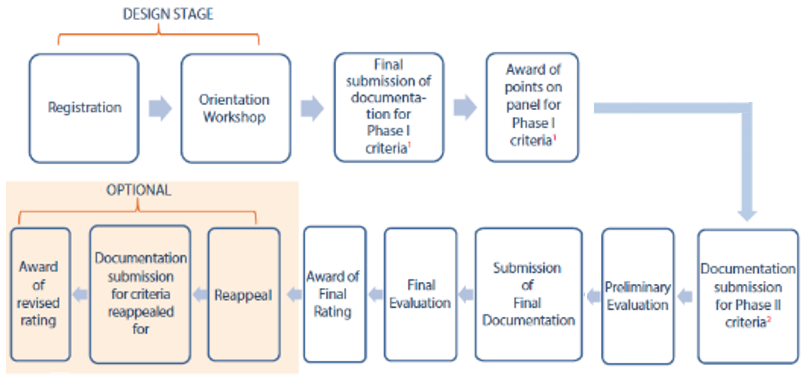
GRIHA Precertification Rating Process
GRIHA Precertification Rating Thresholds
Fast-Track Registration Process
The fast-track process is intended to provide handholding support to projects that need a faster clearance for various business and government approvals. It reduces the time required for rating while maintaining the integrity and accuracy of the GRIHA rating system.
| Review Stage | Review Process | Fast Track |
|---|---|---|
| Review of First Submission | Within 15-20 working days | Within 5-7 working days |
| Final Review | Done within 10-25 working days after receipt of second documentation | Will be done within 3-5 working days after receipt of second documentation |
Fast Track Fees: Rs. 10 lakhs (Exclusive of GST).
Criterion with Weightages
| S.No. | Section Name | Criterion No. | Criterion Name | Criterion Brief | Max. Points | Section Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sustainable Site Planning | 1 | Green Infrastructure | Promote site planning that integrates vegetation, permeable surfaces, and natural drainage to enhance ecological value and reduce environmental impact. | 5 | 12 |
| 2 | Low Impact Design | Minimize alterations to the site by retaining natural features, reducing earthwork, and limiting disruption to existing ecosystems. | 5 | |||
| 3 | Design to Mitigate UHIE | Use shading, reflective materials, and green cover to reduce surface and ambient temperatures, mitigating the Urban Heat Island Effect. | 2 | |||
| 2 | Construction Management | 4 | Air and Soil Pollution Control | Implement dust suppression, soil erosion prevention, and pollution control measures during construction. | 1 | 4 |
| 5 | Topsoil Preservation | Conserve and reuse fertile topsoil for landscaping and site restoration after construction. | 1 | |||
| 6 | Construction Management Practices | Adopt sustainable construction practices, including waste minimization, material storage, and worker safety. | 2 | |||
| 3 | Energy Efficiency | 7 | Energy Optimization | Optimize building energy use through passive design, efficient systems, and performance simulation. | 12 | 18 |
| 8 | Renewable Energy Utilization | Integrate on-site or off-site renewable energy sources to meet part of the building’s energy demand. | 5 | |||
| 9 | Low ODP and GWP Materials | Use insulation, refrigerants, and other materials with low ozone depletion and global warming potential. | 1 | |||
| 4 | Occupant Comfort | 10 | Visual Comfort | Ensure adequate natural daylight, glare control, and quality views for building occupants. | 4 | 12 |
| 11 | Thermal and Acoustic Comfort | Maintain comfortable indoor temperature and sound levels through effective design and systems | 1 | |||
| 2 | Maintaining Good IAQ | Ensure healthy indoor air quality through ventilation, pollutant control, and material selection. | 6 | |||
| 5 | Water Management | 13 | Water Demand Reduction | Reduce potable water demand through low-flow fixtures, water-efficient landscaping, and reuse. | 3 | 16 |
| 14 | Wastewater Treatment | Treat and reuse wastewater on-site to reduce discharge and freshwater demand. | 3 | |||
| 15 | Rainwater Management | Harvest and manage rainwater for reuse and aquifer recharge, minimizing surface runoff. | 5 | |||
| 16 | Water Quality and Self-Sufficiency | Ensure safe water quality and promote self-sufficiency through alternate sources like rainwater and treated wastewater. | 5 | |||
| 6 | Solid Waste Management | 17 | Waste Management – Post Occupancy | Provide infrastructure for segregation, collection, and disposal of waste after occupancy. | 4 | 6 |
| 18 | Organic Waste Treatment On-Site | Treat biodegradable waste within the premises through composting or biogas systems. | 2 | |||
| 7 | Sustainable Building Materials | 19 | Utilization of Alternative Materials in Building | Use recycled, rapidly renewable, or locally sourced materials to reduce environmental footprint. | 5 | 12 |
| 20 | Reduction in GWP through Life Cycle Assessment | Assess and lower the embodied carbon of materials through life cycle analysis. | 5 | |||
| 21 | Alternative Materials for External Site Development | Use sustainable materials for pavements, landscaping, and site infrastructure. | 2 | |||
| 8 | Life Cycle Costing | 22 | Life Cycle Cost Analysis | Evaluate project costs over its life span to ensure economic sustainability and performance efficiency. | 5 | 5 |
| 9 | Safety and Sanitation for Construction Workers | 23 | Water Demand Reduction | Provide safe working conditions, sanitation facilities, and welfare measures for workers. | 1 | 18 |
| 24 | Universal Accessibility | Ensure barrier-free access for persons with disabilities and the elderly. | 2 | |||
| 25 | Dedicated Facilities for Service Staff | Provide appropriate facilities for maintenance and service staff within the project. | 2 | |||
| 26 | Positive Social Impact | Implement measures that benefit local communities, such as employment or shared infrastructure. | 3 | |||
| 10 | Performance Metering and Monitoring | 27 | Commissioning for Final Rating | Verify and optimize building systems before occupancy to ensure design intent is met. | 7 | 7 |
| 28 | Smart Metering and Monitoring | Install smart systems to monitor and manage building energy and water usage. | 0 | |||
| 29 | Operation and Maintenance Protocol | Develop protocols for effective operation, maintenance, and performance tracking. | 0 | |||
| 11 | Innovation | 27 | Innovation | Reward innovative strategies and technologies that enhance sustainability beyond core criteria. | 5 | 5 |
| Grand Total (5 points of innovation are above 100 points) | 100+5 | 100+5 | ||||
Rating Fees
Fee Summary
The fee for the GRIHA Precertification is Rs 1,00,000/- (Exclusive of GST).
