GRIHA for Cities Rating:
The GRIHA for CITIES rating has been structured as a framework for sustainable development of a city, to be achieved by measuring 'greenness' of existing as well as proposed cities.
GRIHA for Cities Rating:
The GRIHA for CITIES rating has been structured as a framework for sustainable development of a city, to be achieved by measuring 'greenness' of existing as well as proposed cities.
The rating intends to develop a qualitative and quantitative criteria integrated in the framework to cover diverse aspects of sustainable development. The rating is in synchronization with the work being done to achieve targets of Sustainable Development Goals, UNFCCC. Furthermore, specifically the work being done in the country through MoHUA's Livability Index, Ease of Living Index and smart cities initiatives.
The rating has been structured as a framework for sustainable development of a city, to be achieved by measuring ‘greenness’ of existing as well as proposed cities.
The rating sets out precepts for planning to achieve holistic sustainability in a city.
Have been integrated in the rating to cover diverse aspects of sustainable development. The rating sets performance benchmarks for key resources, such as energy, water, and waste; and evaluates the project’s performance in areas, such as smart governance, social well-being, and transportation.
The rating is in synchronization with the work being done to achieve targets of Sustainable Development Goals.
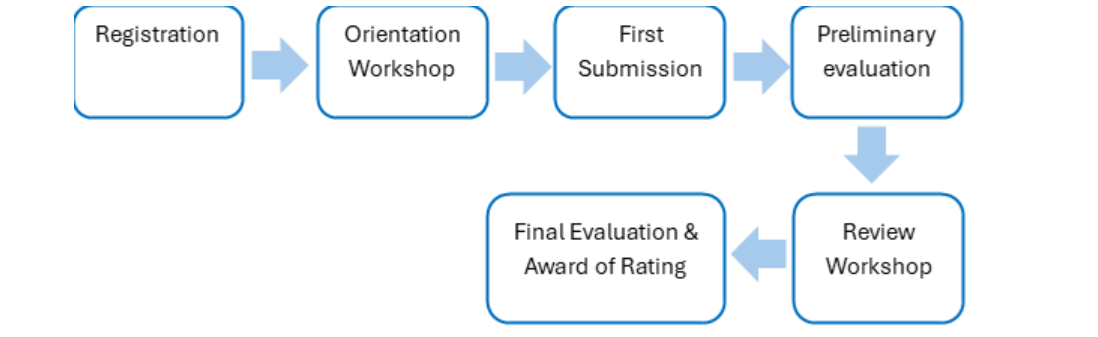
GRIHA for CITIES rating aims to provide a single platform with a set of predefined parameters to compare the performance of various cities/municipalities within the country thereby providing a sustainability accreditation.
The rating helps to increase the marketability of municipalities for investors and enhances their Credit rating. It also aids the civic bodies in becoming torchbearers for the upcoming towns and cities.
Not provided
| Sections | Criterion No. | Criterion Name | Max Points | Section Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section 1: Smart Governance | 1 | Public Participation in Decision Making Processes | 6 | 16 |
| 2 | Intelligent Building Processes | 4 | ||
| 3 | Municipal Finance | 4 | ||
| 4 | Capacity Building | 2 | ||
| Section 2: Water Supply and Management | 5 | Water Sufficiency | 8 | 20 |
| 6 | Water Quality and Charge Collection Efficiency | 6 | ||
| 7 | Stormwater Management | 6 | ||
| Section 3: Sanitation and Municipal Solid Waste Management | 8 | Sanitation and Wastewater | 10 | 18 |
| 9 | Extent of Waste Collection and Management | 6 | ||
| 10 | Waste Recycling/Treatment | 2 | ||
| Section 4: Sustainable Mobility | 11 | Public Transport Facilities | 5 | 18 |
| 12 | Non-Motorized Transport Facilities | 5 | ||
| 13 | Road Safety Measures | 3 | ||
| 14 | Low Carbon Interventions | 2 | ||
| 15 | Policy Measures | 3 | ||
| Section 5: Energy Optimization and Management | 16 | Demand Side Management | 2 | 16 |
| 17 | Managing Household Electricity Consumption | 4 | ||
| 18 | Promoting Energy Efficient Street Lights | 3 | ||
| 19 | Enhancing Power Quality | 3 | ||
| 20 | Promoting Use of Renewable Energy | 4 | ||
| Section 6: Quality of Life | 21 | Universal Accessibility | 3 | 12 |
| 22 | Availability of Public Spaces and Green Areas | 2 | ||
| 23 | Levels of Ambient Air Quality and Noise Quality | 4 | ||
| Section 7: Bonus points | 24 | Provision of Affordable Housing | 3 | 4 |
| 25 | Bonus Points | 4 | ||
| Grand total (Bonus Points are over and above 100 points) | 100 + 4 | 100 + 4 | ||
The fee for rating system is mentioned below:
| Area under the purview of civic body | Registration cum rating fees |
|---|---|
| Up to 25 sq km | INR 7,50,000 |
| Between 26 – 100 sq km | INR 9,00,000 |
| Above 101 sq km | INR 11,00,000 |